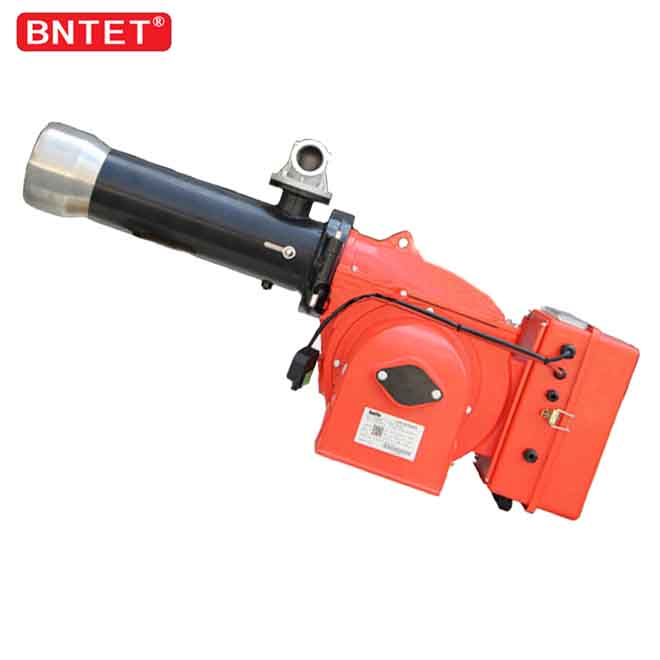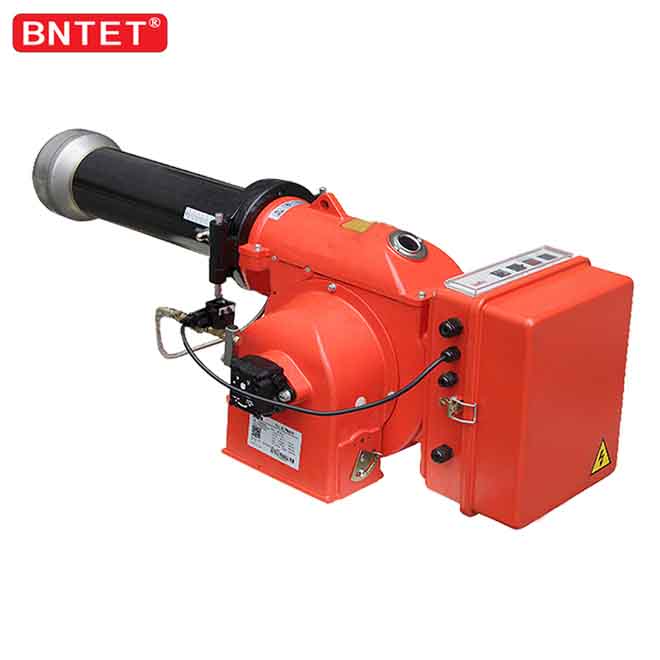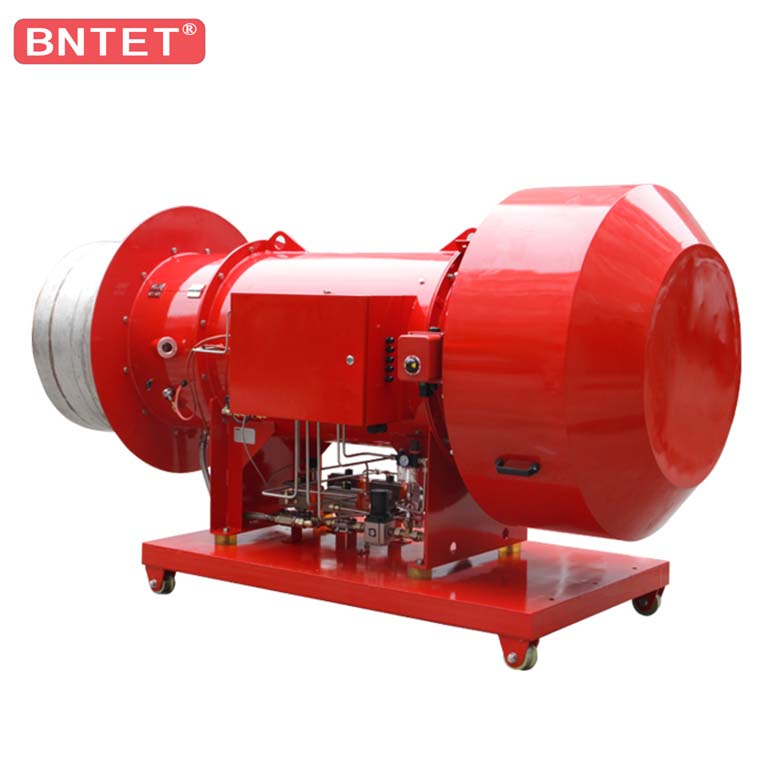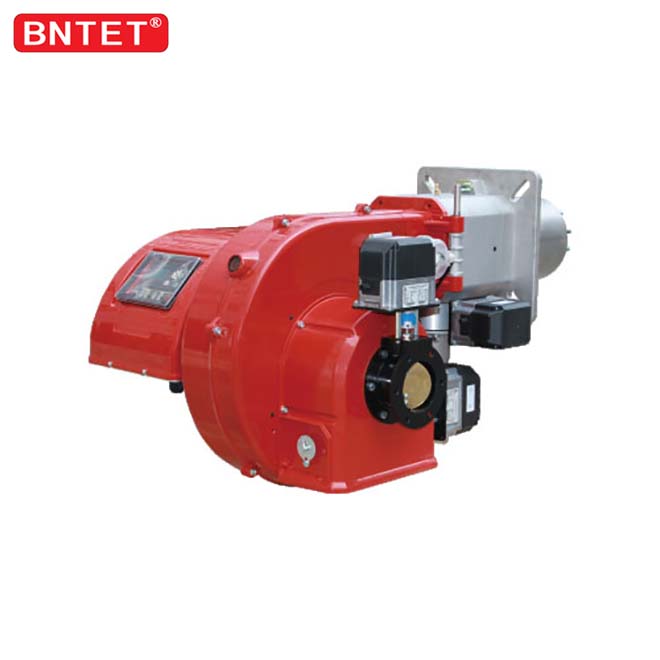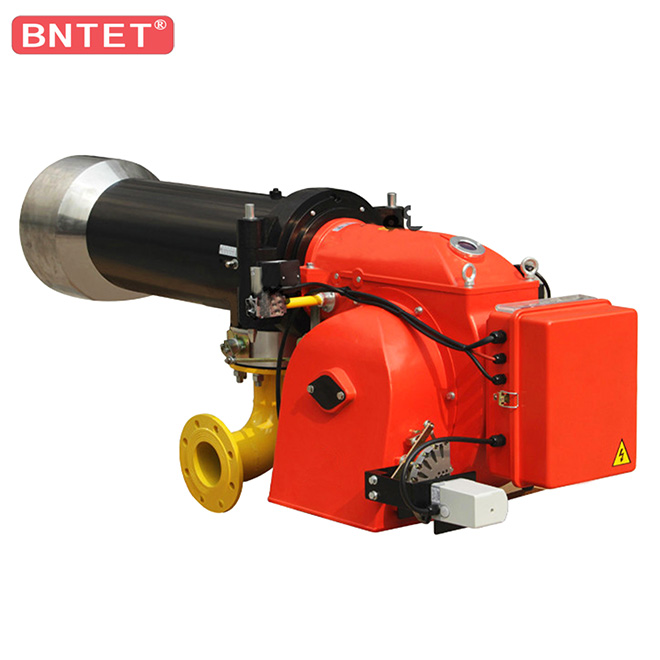
Safety system of industry dual fuel oil gas boiler burner
If a large amount of combustible gas accumulates in the oil-gas boiler (such as gas leakage or fuel evaporation in the high-temperature furnace) and reaches the blasting limit, deflagration will occur during combustion, posing a serious threat to the safety of the oil-gas boiler.
The so-called blasting limit refers to the scale of high-speed combustion concentration (generally referred to as volume concentration) that can occur when gas or fuel vapor is mixed with air. The lowest value of this scale is called the lower limit of blasting, and the highest value is called the upper limit of blasting. Under normal circumstances, the blasting limit of natural gas is 3%~15%; coke oven gas is 5%~36%; liquefied petroleum gas is 1.6%~11.1%. The larger the scale of the blasting limit and the lower the lower limit of blasting, the greater the risk of blasting.
In order to prevent the fuel gas from leaking into the furnace and forming a safety hazard, the burners are equipped with corresponding automatic combustion procedures, flameout maintenance devices and other safety maintenance systems. Generally, the oil-gas burner has a pre-purge time before combustion, that is, before the combustion arc is generated, the burner fan has a purge process in the furnace.
In this process, the combustible gas that may still remain inside the furnace can be discharged out of the furnace, so as to avoid the occurrence of deflagration. In addition, during the operation of the oil and gas burner, if the flame subsides but the fuel delivery continues, a large amount of combustible materials (gas or oil gas) will also accumulate in the furnace, posing a risk. Therefore, oil and gas burners have a flame monitoring system to maintain the system when the flame is out, that is, immediately stop the operation of the burner when the flame is out. There are two commonly used flame monitoring methods. The presence or absence of flame can be confirmed by ionization method or ultraviolet detection method.







